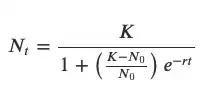The fitting function growthcurver::SummarizeGrowth is wrapped around Nonlinear Least Squares model minpack.lm::nlsLM, which provides statistics on parameter estimations similar to lm. The NLS model is returned in $mod and is consistent with the returned statistics for K, N0, r.
So K, N0, r are in the sort of standard estimate +/- critical value*se form. The critical value is determined by the t distribution with the residual degree of freedom (sample size - # parameters). In the example below, the critical value is 2.010635.
#example from the package
library(growthcurver)
set.seed(1)
k_in <- 0.5
n0_in <- 1e-5
r_in <- 1.2
N <- 50
data_t <- 0:N * 24 / N
data_n <- NAtT(k = k_in, n0 = n0_in, r = r_in, t = data_t) +
rnorm(N+1, sd=k_in/10) #add noise
# Model fit
gc <- SummarizeGrowth(data_t, data_n)
summary(gc$mod) # returned nlsLM model
# Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#k 0.608629 0.013334 45.643 < 2e-16 ***
#n0 0.005795 0.003208 1.806 0.0772 .
#r 0.563808 0.068195 8.268 8.71e-11 ***
#Residual standard error: 0.05935 on 48 degrees of freedom
# Extracted p-value for n0 matches above
gc$vals$n0_p
> 0.07715446
# The p-value can be calculated by t-distribution
pt(gc$vals$n0 / gc$vals$n0_se, df=gc$vals$df, lower.tail=FALSE) * 2
> 0.07715446
# 95% confidence interval by t-distribution
qt(0.975, gc$vals$df)
> 2.010635
gc$vals$n0 + qt(0.975, gc$vals$df) * gc$vals$n0_se
> 0.01224516
gc$vals$n0 - qt(0.975, gc$vals$df) * gc$vals$n0_se
> -0.0006557696