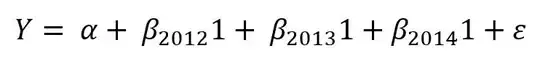You can just do a Wald test on the coefficients directly or via margins:
. sysuse auto
(1978 Automobile Data)
. qreg price i.rep78, quantile(0.5) nolog
Median regression Number of obs = 69
Raw sum of deviations 65163 (about 5079)
Min sum of deviations 63340 Pseudo R2 = 0.0280
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
price | Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
rep78 |
2 | 170 1745.715 0.10 0.923 -3317.467 3657.467
3 | -185 1612.622 -0.11 0.909 -3406.584 3036.584
4 | 864 1645.876 0.52 0.601 -2424.015 4152.015
5 | 463 1697.437 0.27 0.786 -2928.02 3854.02
|
_cons | 4934 1561.415 3.16 0.002 1814.715 8053.285
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
. test _b[5.rep78] = _b[3.rep78]
( 1) - 3.rep78 + 5.rep78 = 0
F( 1, 64) = 0.69
Prob > F = 0.4082
. margins rep78, pwcompare(pveffects)
Warning: cannot perform check for estimable functions.
Pairwise comparisons of adjusted predictions
Model VCE : IID
Expression : Linear prediction, predict()
-----------------------------------------------------
| Delta-method Unadjusted
| Contrast Std. Err. z P>|z|
-------------+---------------------------------------
rep78 |
2 vs 1 | 170 1745.715 0.10 0.922
3 vs 1 | -185 1612.622 -0.11 0.909
4 vs 1 | 864 1645.876 0.52 0.600
5 vs 1 | 463 1697.437 0.27 0.785
3 vs 2 | -355 878.6573 -0.40 0.686
4 vs 2 | 694 938.2936 0.74 0.460
5 vs 2 | 293 1026.051 0.29 0.775
4 vs 3 | 1049 658.3504 1.59 0.111
5 vs 3 | 648 778.3381 0.83 0.405
5 vs 4 | -401 845.0837 -0.47 0.635
-----------------------------------------------------
Edit:
You can do a one-sided test like this:
qreg price i.rep78, quantile(0.5) nolog
local sign_diff = sign(_b[5.rep78] - _b[3.rep78])
testnl _b[5.rep78] - _b[3.rep78] = 0
display "H_0: _b[5.rep78] >= _b[3.rep78] p-value = " normal(`sign_diff'*sqrt(r(chi2)))
or perhaps like this:
qreg price i.rep78, quantile(0.5) nolog
local sign_diff = sign(_b[5.rep78] -_b[3.rep78])
test _b[5.rep78] = _b[3.rep78]
display "H_0: _b[5.rep78] >= _b[3.rep78] p-value = " 1-ttail(r(df_r),`sign_diff'*sqrt(r(F)))