Whether above solution is correct
Yes.
How to get the mean and sd for $P(X|X<Y)$ and $P(X|X>Y)$ if they are still normal?
They are not normal.
Proof:
Given $P(X | X>Y) = \frac{\Phi(\frac{x-\mu_2}{\sigma_2})\phi_x(\mu_1,\sigma_1)}{1-\Phi(\frac{\mu_2-\mu_1}{\sqrt{\sigma_2^2+\sigma_1^2}})}$ is equivalent to a product of a uniform random variable $(\Phi(\frac{x-\mu_2}{\sigma_2})$ and a normal random variable $(\phi_x(\mu_1,\sigma_1))$
Consider $X_1 \sim N(0, 1)$ and $X_2 \sim U(0,1)$, then the product $Z = X_1X_2$ distrobution is given by:
\begin{align*}
F_Z(z) &= P(Z \leq z)\\
&= P(X_1X_2 \leq z)\\
&= \int_{X_1\geq 0}P(X_2 \leq \frac{z}{x_1}) \phi_{X_1}(x_1)\ dx_1 +\int_{X_1\leq 0}P(X_2 \geq \frac{z}{x_1}) \phi_{X_1}(x_1)\ dx_1\\
&= \int_{X_1\geq 0}\frac{z}{x_1} \phi_{X_1}(x_1)\ dx_1 + \int_{X_1\leq 0}(1-\frac{z}{x_1}) \phi_{X_1}(x_1)\ dx_1\\
&= \frac{1}{2} + \int_{X_1\geq 0}\frac{z}{x_1} \phi_{X_1}(x_1)\ dx_1 - \int_{X_1\leq 0}\frac{z}{x_1} \phi_{X_1}(x_1)\ dx_1 \\
&= \frac{1}{2} + \int\frac{2z}{x_1} \phi_{X_1}(x_1)\ dx_1
\end{align*}
which does not mimick CDF of a normal.
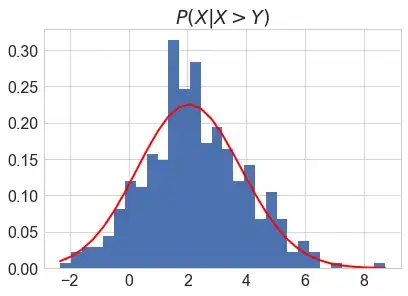
You can however still check if your solution is correct by simulation:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy as sp
import numpy as np
mu1 = 1
sigma1 = 2
mu2 = 2
sigma2 = 3
np.random.seed(42)
X = np.random.normal(mu1, sigma1, 1000)
Y = np.random.normal(mu2, sigma2, 1000)
# P(X|X>Y)
P_X_XgY = X[X>Y]
# P(X|X<Y)
P_X_XlY = X[X<Y]
denom = 1-sp.stats.norm.cdf((mu2-mu1)/np.sqrt(sigma1**2+sigma2**2))
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(P_X_XgY, 30, normed=True)
plt.plot(bins, 1/(sigma1 * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi)) * \
(sp.stats.norm.cdf((bins-mu2)/sigma2)/denom) *\
np.exp( - (bins - mu1)**2 / (2 * sigma1**2) ), linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.title('$P(X|X>Y)$')
denom = sp.stats.norm.cdf((mu2-mu1)/np.sqrt(sigma1**2+sigma2**2))
count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(P_X_XlY, 30, normed=True)
plt.plot(bins, 1/(sigma1 * np.sqrt(2 * np.pi)) *\
((1-sp.stats.norm.cdf((bins-mu2)/sigma2))/denom) *\
np.exp( - (bins - mu1)**2 / (2 * sigma1**2) ), linewidth=2, color='r')
plt.title('$P(X|X<Y)$')