In relation to a recent post about what analyses to conduct for a data set, I am now asking a related question about the test to run in SPSS.
Background information on the data:
- Repeated measures design with count data
- Participants responded about the number of intrusions they had after exposure to two conditions.
- Data ranges from 0 to 4, with mostly zeroes, and thus is positively skewed.
- Thus, I will want to do an analysis for Poisson distributed data.
Question
What analysis would be ideal to carry out for the above data?
My take on issue
One idea was to carry out a generalised linear models analysis with a Poisson loglinear model.
- However, the issue here seems to be that there is only one dependent variable that can be inserted but I have two (see image below).
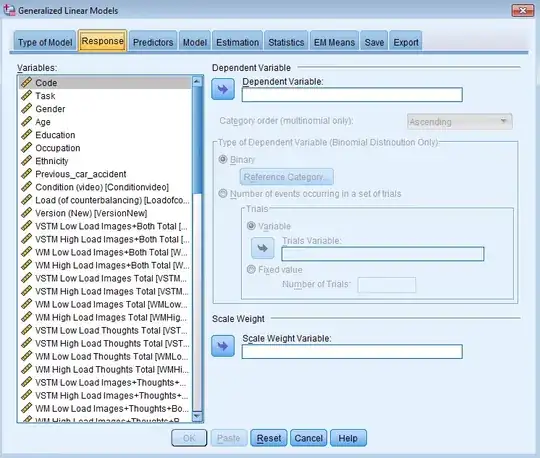 Image 1 - Generalised Linear Model with Poisson Loglinear Model - only one DV option
Image 1 - Generalised Linear Model with Poisson Loglinear Model - only one DV option
- Another idea was to find the difference between the two variables, followed by dividing the answer by the square root of the number of values (in this case 2) to produce a composite score of the two variables.
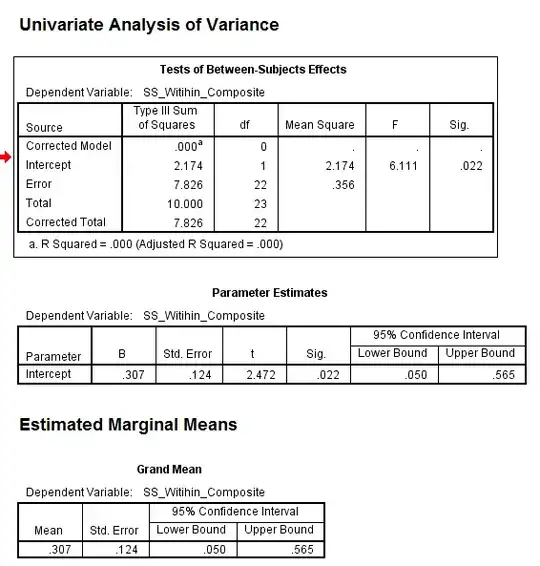 Image 2 Image 2 - Univariate ANOVA - is it right for count, non-parametric data?
Image 2 Image 2 - Univariate ANOVA - is it right for count, non-parametric data?
After I ran a univariate ANOVA which produced significant results (see image above). However, the problem with this idea is that:
- (a) I do not use a Poisson distribution.
- (b) If we consider the count data as being non-continuous as the data is non-normally distributed then an ANOVA should not be used.
- (c) In general I am not sure if producing a composite score so that I can run a univariate ANOVA is fine.
Update of information following original post
1. More information about the study DV:
The DV is number of intrusions so yes you are right that it is actually only one DV I just realised meaning perhaps I didn't give a clear explanation (which I will fix in my original post after clarifying I understand). I had the DV of number of intrusions and each participant being exposed to a condition of low levels of information (low load) and high levels of information (high load), and then I wanted to see which condition was associated with the development of more intrusions. I coded the data into two separate columns for # of intrusions (low and high load).
2. Elaboration on the study design
- The study explored whether watching a film, while remembering more stimuli (high load), presented earlier before the film, led to less intrusions than remembering less stimuli (low load).
- The DV was number of intrusions after watching the film.
- The IVs were low and high load which were determined by the number of stimuli a person had to remember whilst watching a film.
- Thus low load (IV 1) should lead to more intrusions (DV) than high load (IV 2).
- All subjects were exposed to both conditions.