I have a discrete signal $x[n]$ of length say $1024$, such that :
$$-1 \leq x[n] \leq 1, \qquad \forall n$$
and let $y[k]$ be its DFT.
Is there an upper bound for $|y[k]|$ ? (i.e. for the DFT of a bounded signal)
You can obtain a bound on the magnitude of the DFT of $x[n]$ ($|x[n]|\le 1$) as follows:
$$\big|X[k]\big|=\left|\sum_{n=0}^{N-1}x[n]e^{-jkn2\pi/N}\right|\le\sum_{n=0}^{N-1}|x[n]|\le N\max_n|x[n]|=N\tag{1}$$
Note that for signals $x[n]=e^{j2\pi nl/N}$, $l\in\mathbb{Z}$, the bound is tight. However, for most other signals with $|x[n]|\le 1$ you will find that the maximum of $|X[k]|$ is substantially smaller than the bound given by $(1)$.
The upper bound would be a coherent summation of all samples of $ x \left [ x \right ] $.
Specifically:
$$\begin{aligned} X \left[ k \right ] & = \sum_{n = 0}^{N - 1} x \left[ n \right] \exp^{-j 2 \pi \frac{nk}{N}} \\ & \leq \left| \sum_{n = 0}^{N - 1} x \left[ n \right] \exp^{-j 2 \pi \frac{nk}{N}} \right| \\ & \leq \sum_{n = 0}^{N - 1} \left| x \left[ n \right] \exp^{-j 2 \pi \frac{nk}{N}} \right| \\ & \leq \sum_{n = 0}^{N - 1} \left| x \left[ n \right] \right| \\ & \leq N \max_{n} \left \{ \left| x \left[ n \right] \right| \right \} \end{aligned}$$
If you add the info $ \forall n \left| x \left[ n \right] \right| \leq 1 $ you can say you're bounded by $ N $.
I hope this helps...
All calculated coefficients of your FFT will be lower than maximum amplitude of your signal. Of course I mean normalized FFT, you must divide each of them by length of your sequence (in case of rectangular window). Two cases you should think of are:
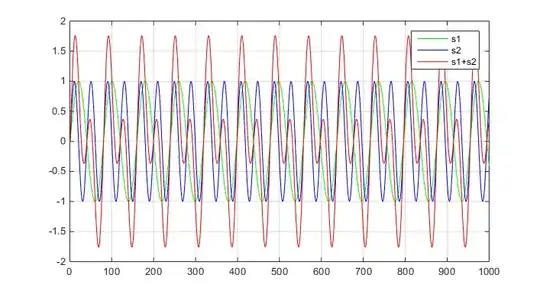
One sinusoid varying between $-1$ and $1$ produces obviously peak in spectrum at its frequency with amplitude of $1$. That's what we expect
You have two (or more) sinusoids, each of them has also unit amplitude. Their superposition might produce signal (your signal $x[n]$ ) with an amplitude higher than $1$. You can observe that on plot below. Although when you do the FFT you will get two separated peaks with amplitude $1$. That means you cannot get signal with spectral peak values higher than time domain amplitude.
In some cases you will also encounter leakage problem, and the amplitude of your peak will be bit lower than it should be. But this also assures that you won't get more than maximum absolute value in the time domain.